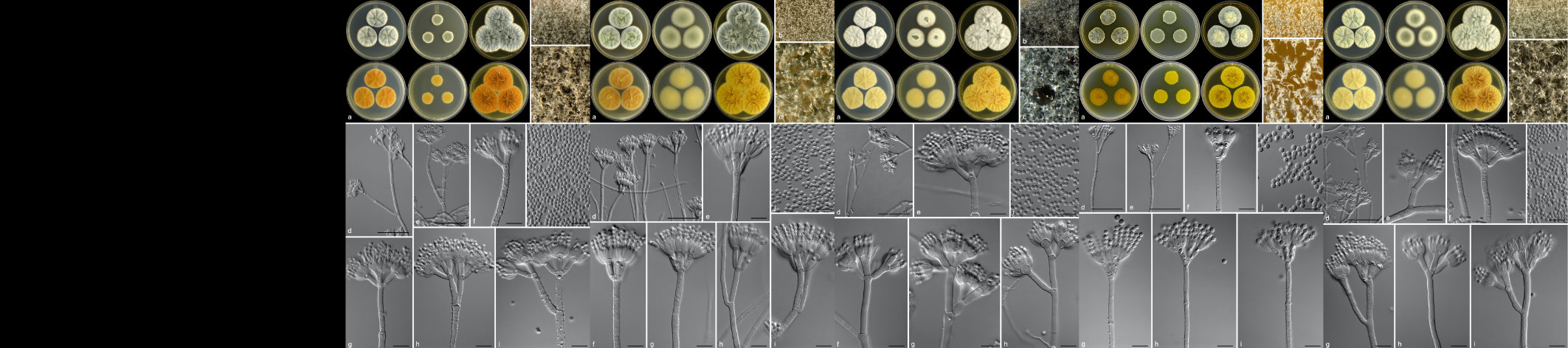
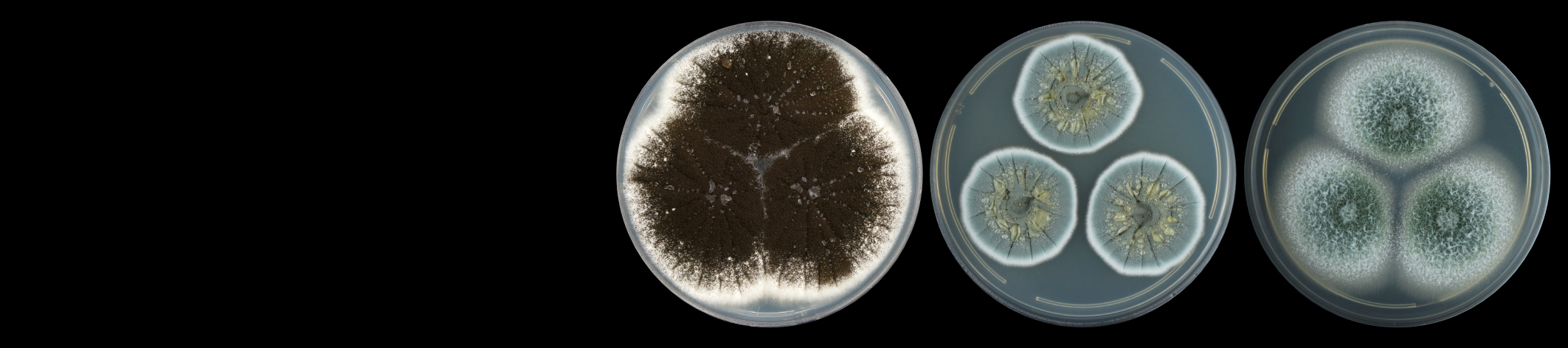
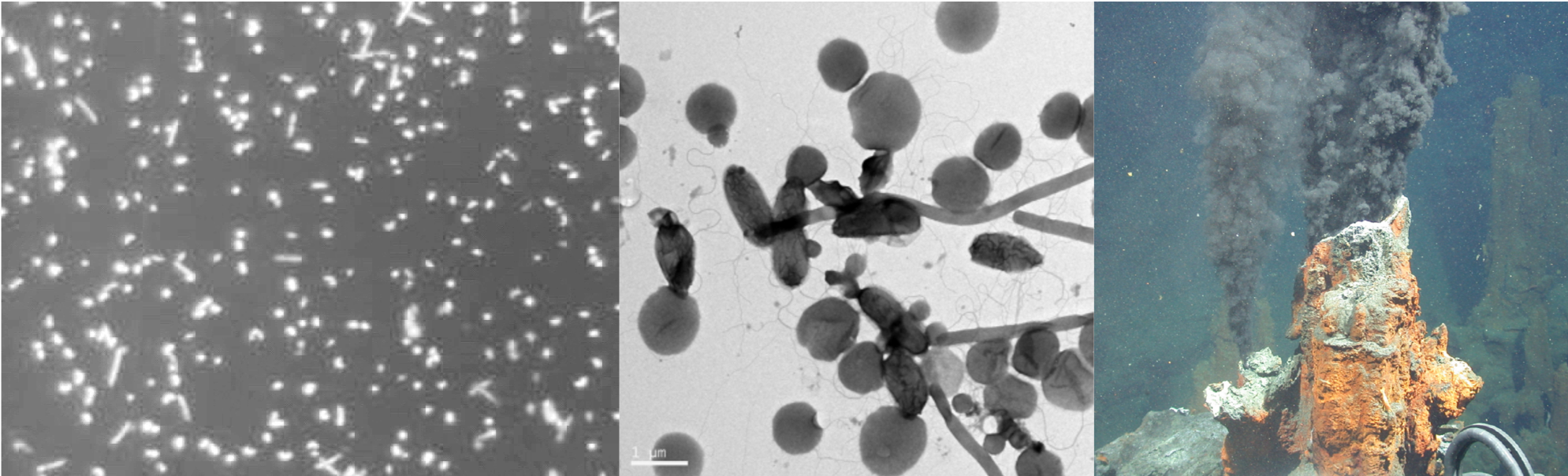
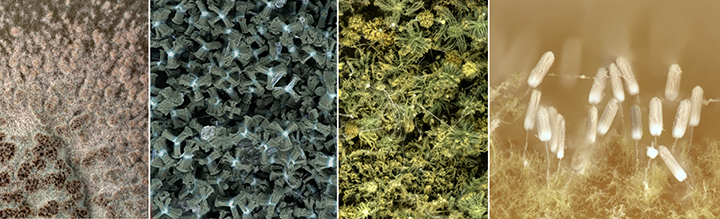
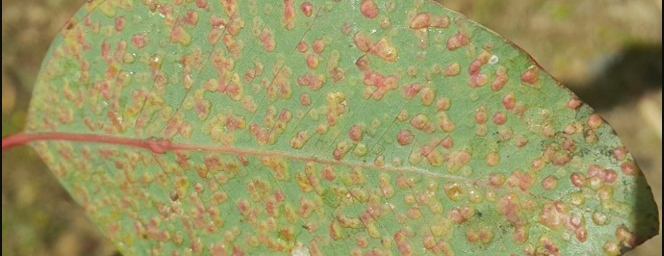
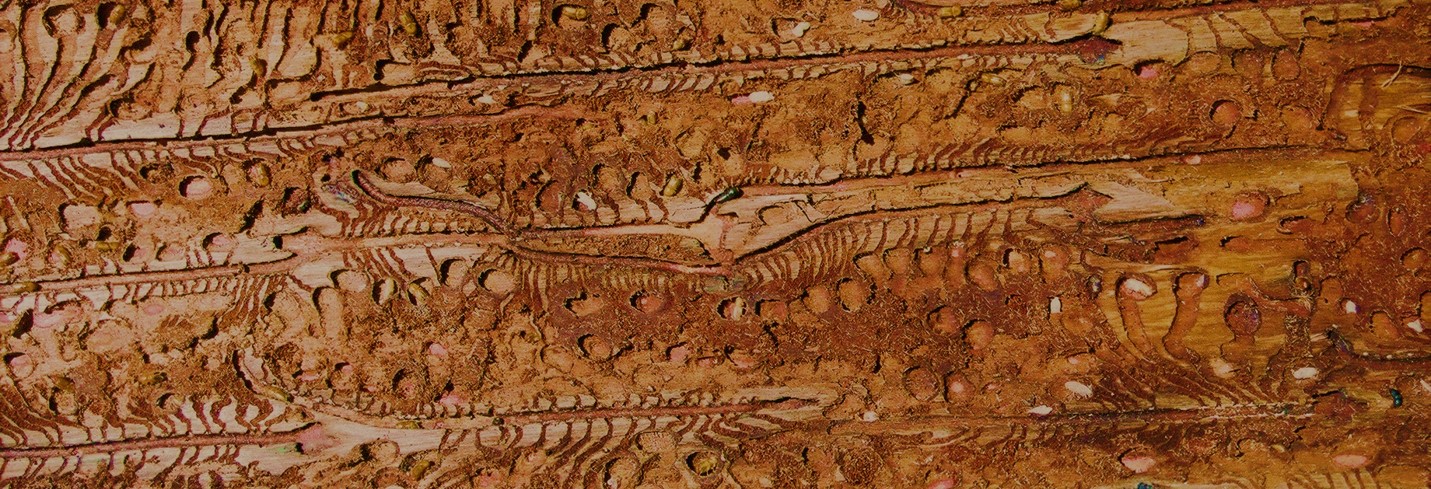
The Tree Protection Co-operative Programme (TPCP) was established based on a very small team of researchers at the University of the Free State and focused on a single threatening Eucalyptus disease problem. The programme has since grown to become highly recognised internationally as the single strongest programme dealing with pest and pathogen problems in plantation forestry in the world. The TPCP has also brought huge energy to agricultural research and education in the biological sciences in South Africa. For example, it formed the foundation for the establishment of the Forestry and Agricultural Biotechnology Institute (FABI) at the University of Pretoria, which has become a flagship research centre promoting many aspects of plant improvement in South Africa.
The TPCP represents a co-operative research initiative between the University of Pretoria and all private forestry companies in South Africa. It is also supported by the South African Government Department of Forestry, Fisheries and Environment. Other than long and short-term research, the TPCP provides members with extension services, training of forestry students at Universities, access to a world-class disease and pest diagnostic clinic and guidance in dealing with tree pest and pathogen problems. One of the key products of the TPCP is to produce biological control agents for insect pests that damage plantations belonging to members. This work depends on outstanding quarantine green house and related facilities.
The TPCP formed the basis for the establishment of the Department of Science and Innovation (DSI)-National Research Foundation (NRF) Centre of Excellence in Plant Health Biotechnology (CPHB). This programme focuses on the health of native South African trees. Given that pests and pathogens are moving from native to non-native plantation trees and vice versa, there is substantial synergy between these two programmes.