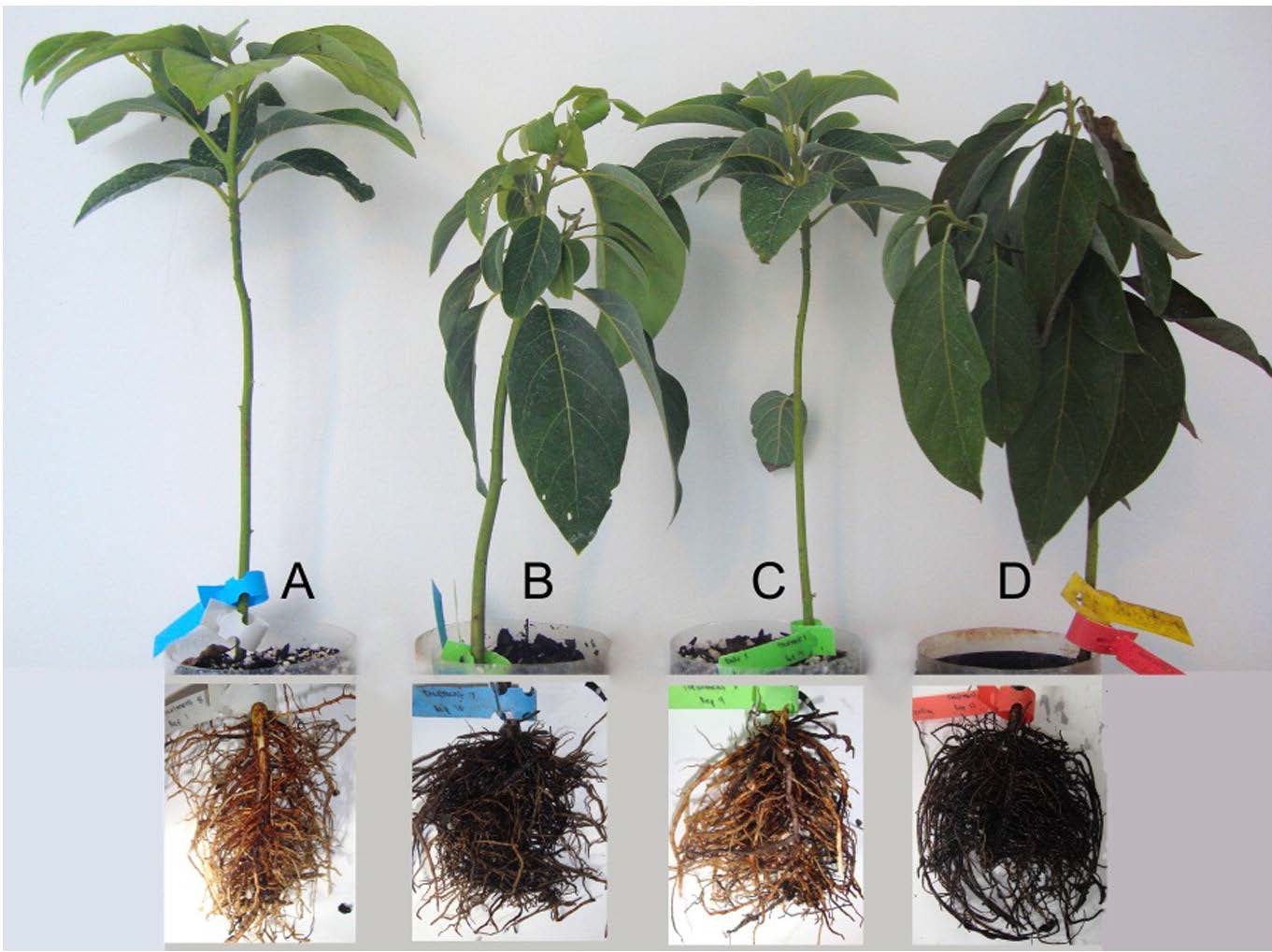
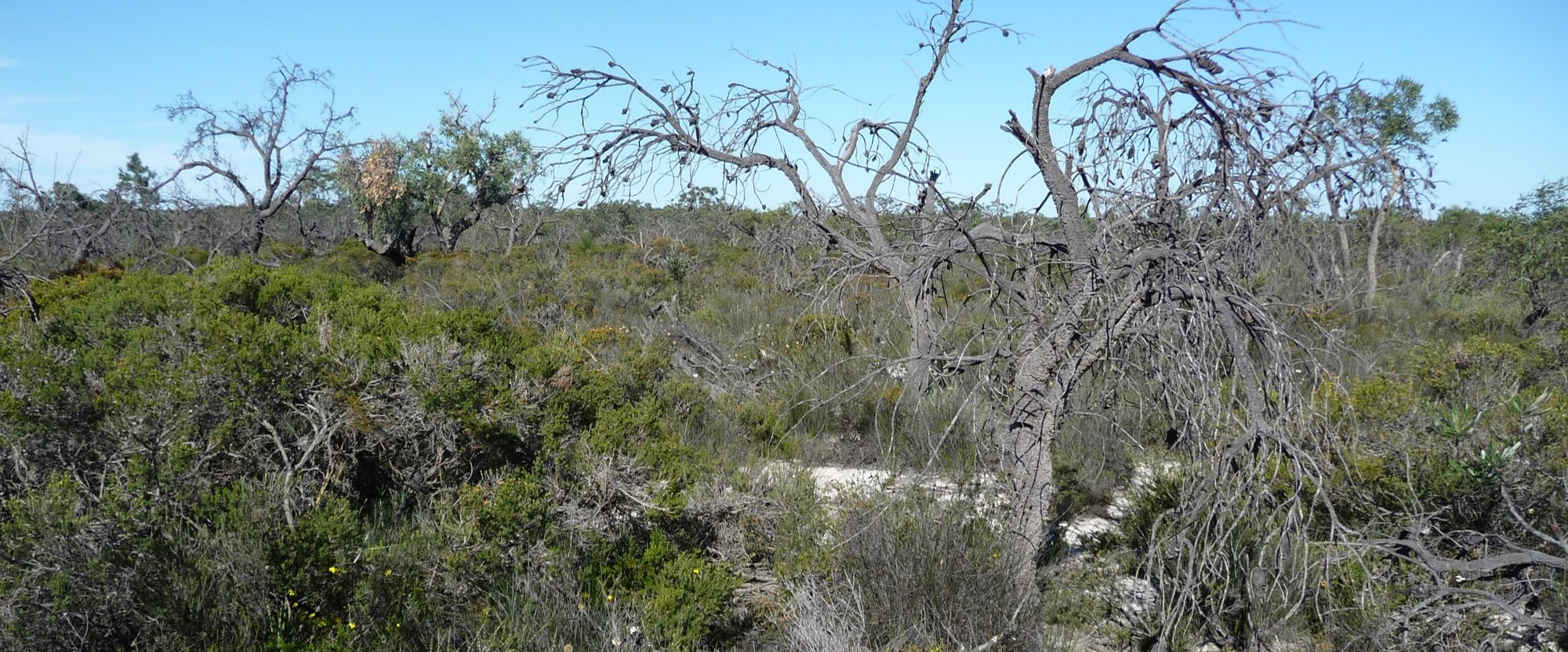
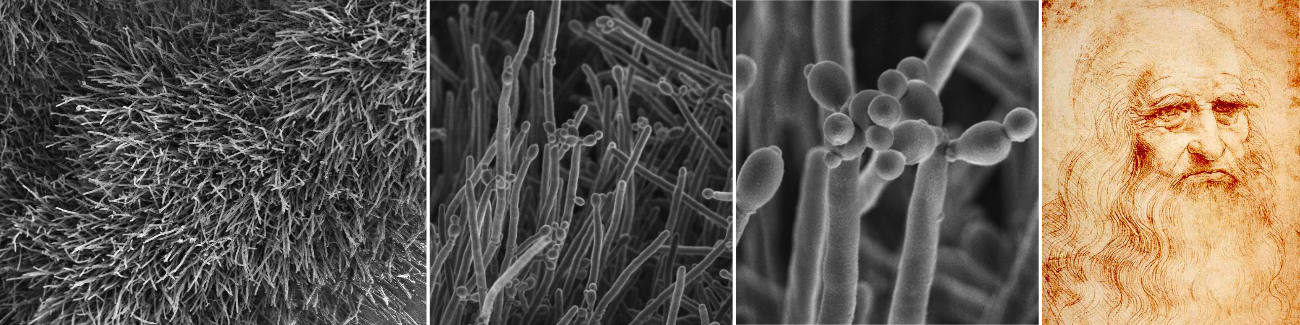
Phytophthora root rot (PRR) is the most severe and damaging disease in avocado plantations in South Africa. The causal agent of PRR is the notorious oomycete, Phytophthora cinnamomi (Pc). This pathogen has an extensive host range making it an economically important plant pathogen. The pathogen is a heterothallic species that can reproduce by sexual or asexual means. Furthermore, Pc is hemibiotrophic, meaning it has an initial biotrophic stage prior to switching to the nectrophic stage at later stages of infection. It can persist in soil or infected plant material for extended periods of time, and there is no means to eradicate this oomycete from infected areas once the pathogen has successfully established in soils. Currently, phosphite injections, along with the use of good agricultural practices, are commonly used as methods of control for PRR.
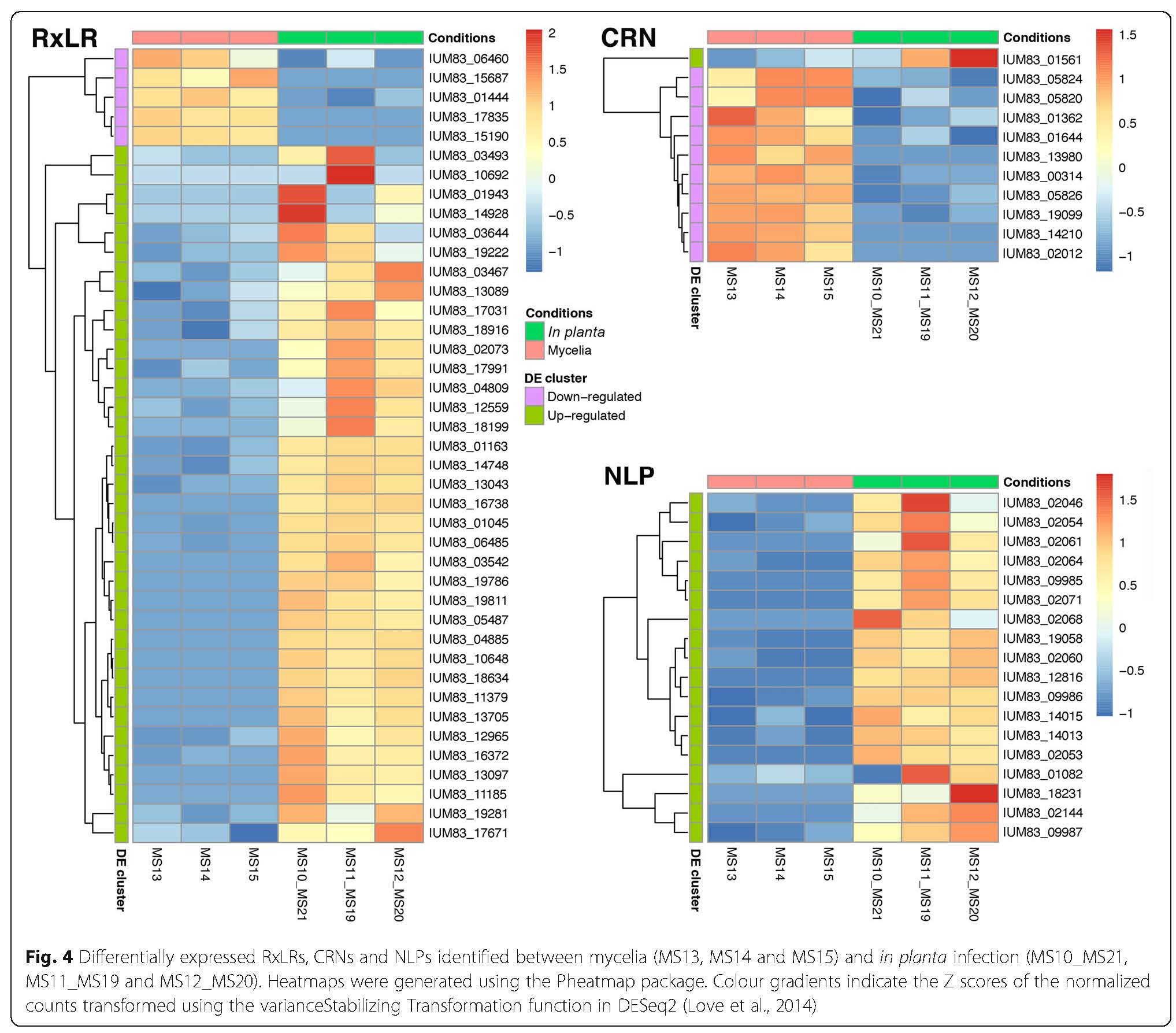
Research within the ARP has provided some insight into the biology, population diversity and the molecular basis for the Pc-avocado interaction. The sequencing of the genome of a South African Pc isolate and the availability of RNA sequencing data from a Pc-avocado infection trial has allowed the group to delve further into understanding how the pathogen is able to manipulate and suppress plant immunity during infection. Current work in the ARP involves identifying and functionally characterising effector genes which are known to play roles during infection. The group is currently on three groups of effectors; the NLPs, RxLRs and Crinklers; and the aim is to determine how these effectors contribute to the pathogenicity of this pathogen and the strategies by which they are able to manipulate or suppress plant immunity to establish infection.
* Read more about Phytophthora cinnamomi on our Fact sheet here.
ARP Team Members
Katelyn Baird: Characterising the role of Phytophthora cinnamomi NLP proteins in plant cell infection.
Ncobile Kunene: Elucidating the role of Phytophthora cinnamomi RxLR effector genes during Persea americana infection.
Kayla Midgley: Characterising the role of Phytophthora cinnamomi CRN effector proteins in host plant cell death.
Susanna Anbu: Expression profiling of Nep-like protein (NLP) effector genes during infection in avocado.