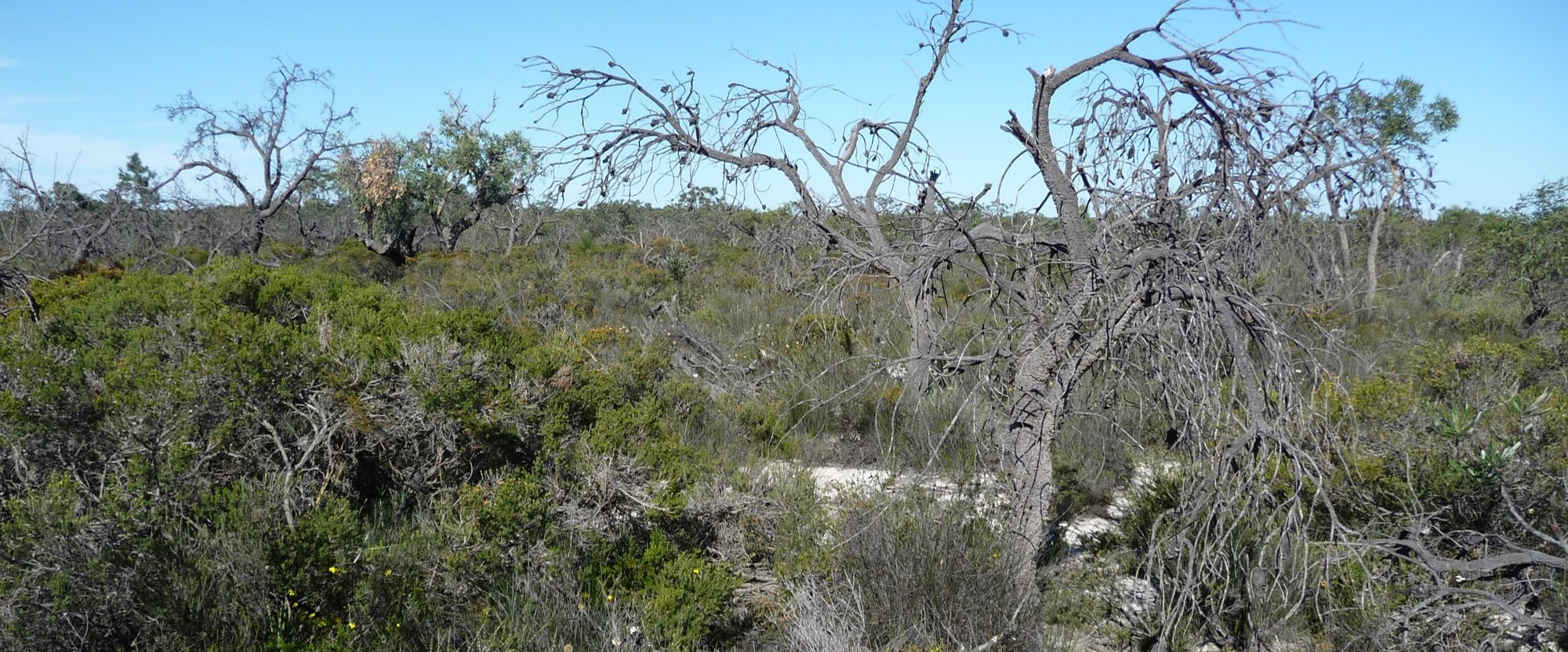
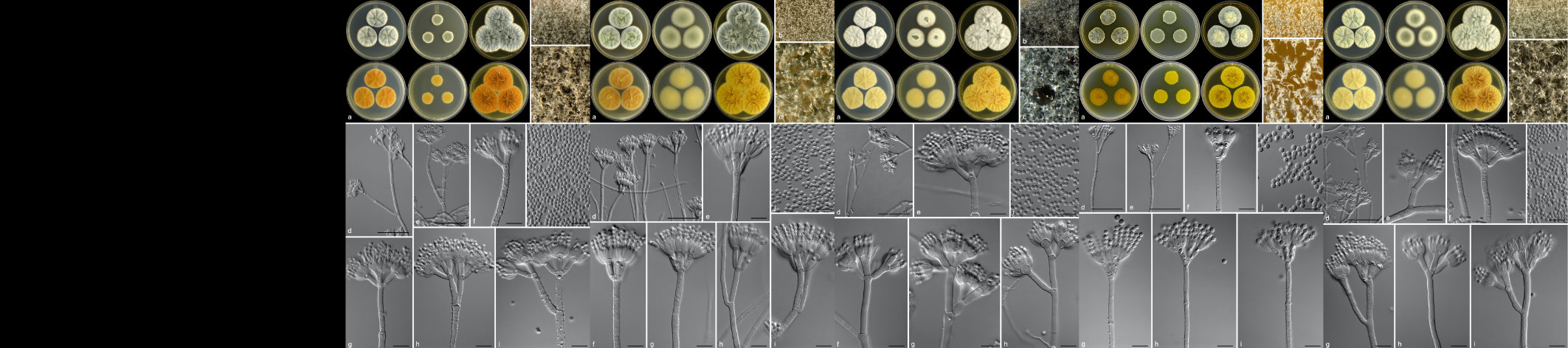
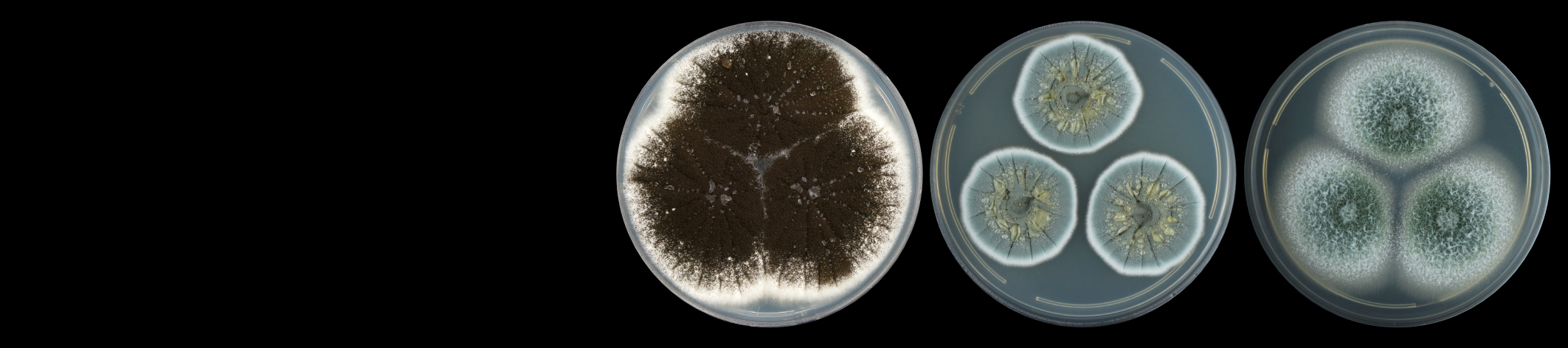
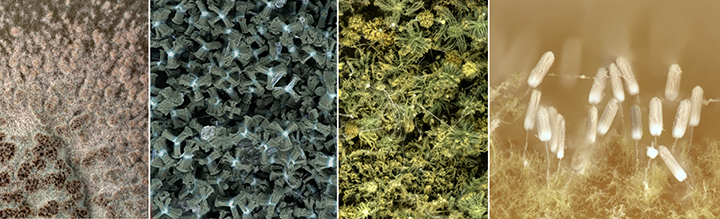
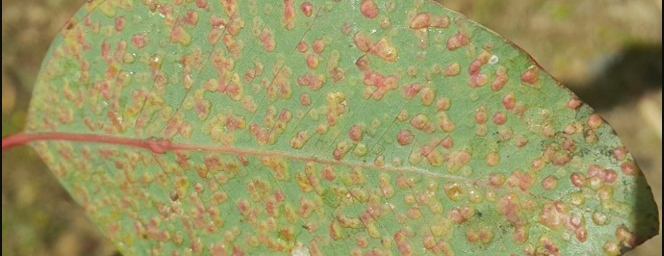
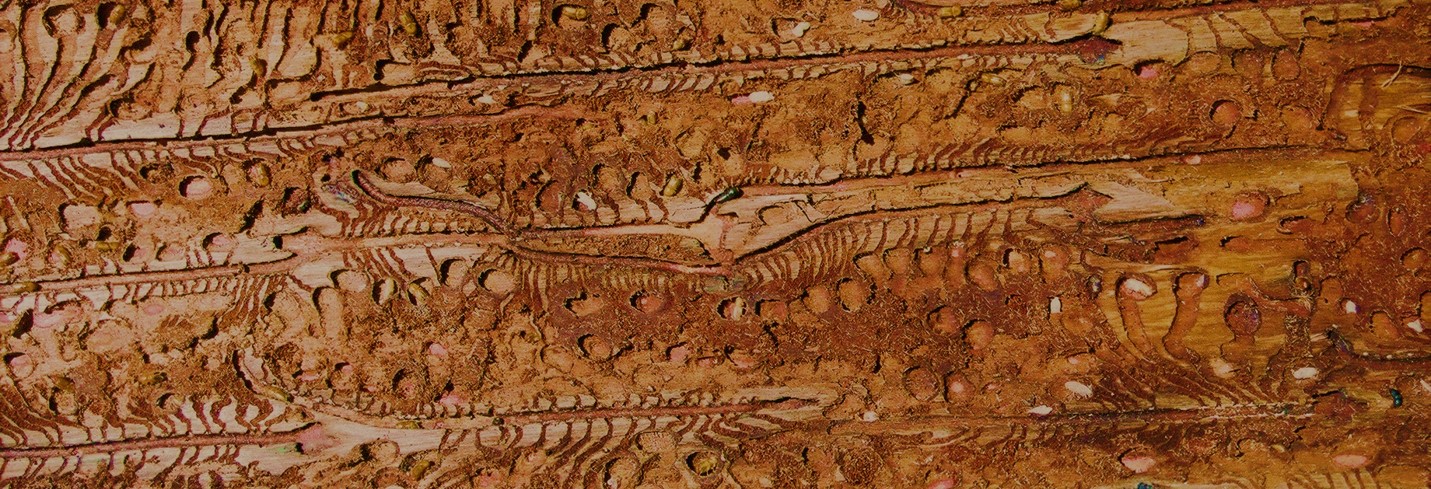
An ambrosia beetle, commonly known as Polyphagous Shot Hole Borer (PSHB) Euwallacea fornicatus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Scolytinae), is considered to be a pest, due to its ability to damage trees by acting as a vector for a pathogenic fungi. Fusarium euwallaceae, the fungal symbiont of the PSHB, is inoculated into the tree by the beetle. Eventually, the fungal symbiont prevents the transport of water and nutrients by invading the xylem, that leads to Fusarium dieback and the eventual death of the host tree. This pest-pathogen complex has emerged as an invasive pest in Israel and the United States of America (California), causing severe damage and significant economic losses to agricultural, ornamental and urban trees, especially to their avocado industries.
This pest-pathogen complex was detected in South Africa damaging Platanus x acerifolia (London Plane) trees in the National Botanical Gardens, KwaZulu-Natal. Recently, it was detected on a backyard tree and in a commercial avocado orchard. Control management strategies for this pest complex are limited due to inefficient trapping mechanisms, lack of biocontrol measures and inefficient fungicides. The use of resistant/tolerant trees could serve as a potential control strategy. Current research within the Avocado Research Programme (ARP) is therefore aimed at identifying Fusarium spp. isolates sampled from avocado trees to determine the extent of the threat to industry, after which the taxonomy of these isolates will be defined. We are also in the process of determining the threat on various, commonly growth avocado cultivars through the use of multiple pathogenicity trials.
*Read more about Ambrosia beetles and Fusarium dieback on our Fact sheet here.
ARP Team Members

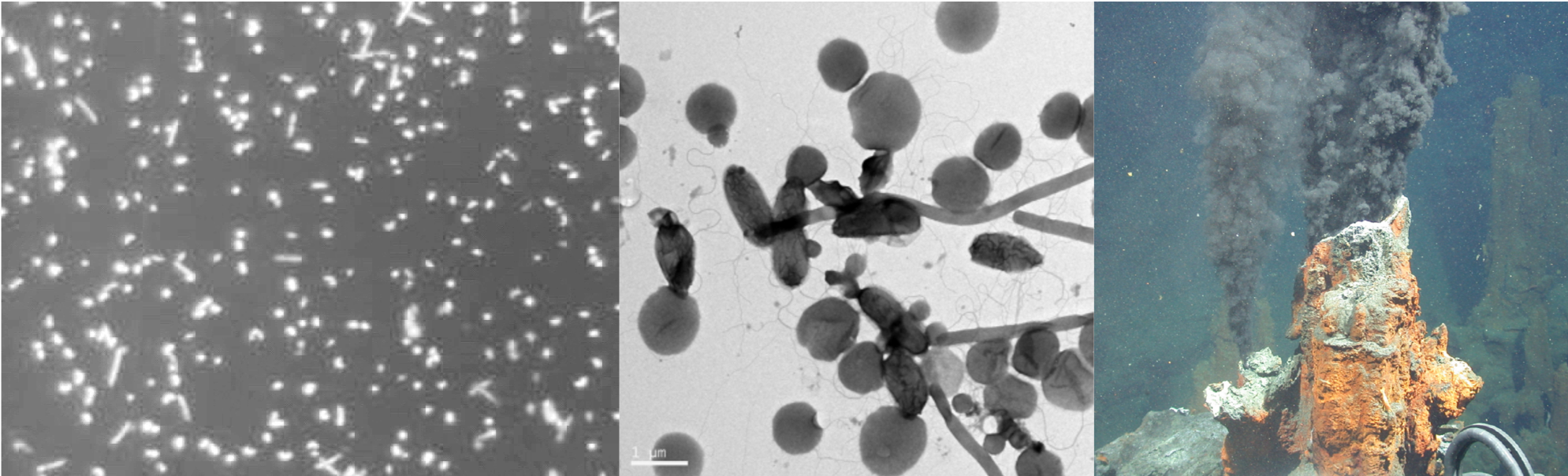
Images from left to right: 1. Xylosandrus crassiusculus fungal symbiont Ambrosiella roeperi in culture. 2. Internal symptoms of PSHB infestation as beetles establish a network of galleries. 3. PSHB interception traps used in orchards.