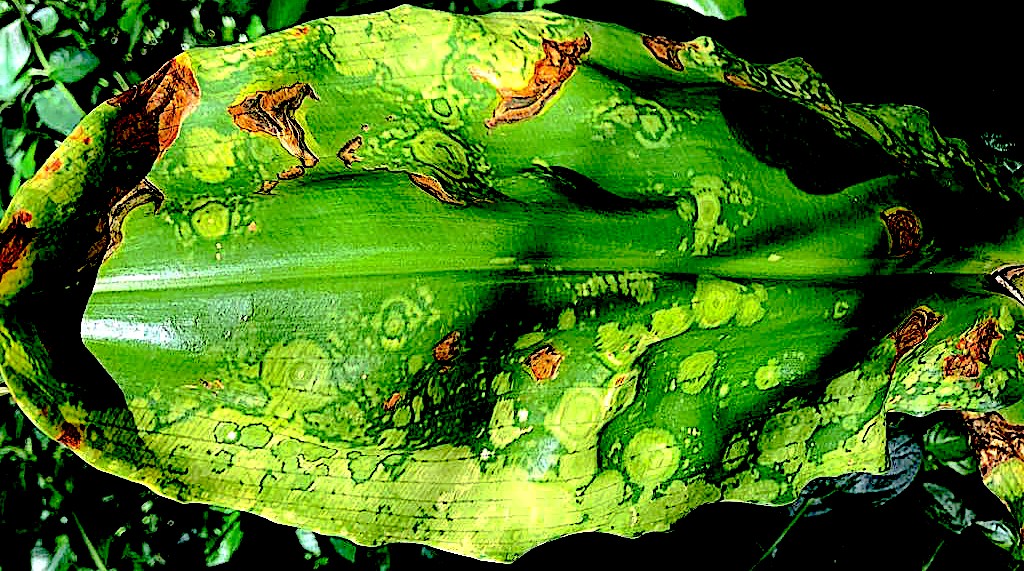
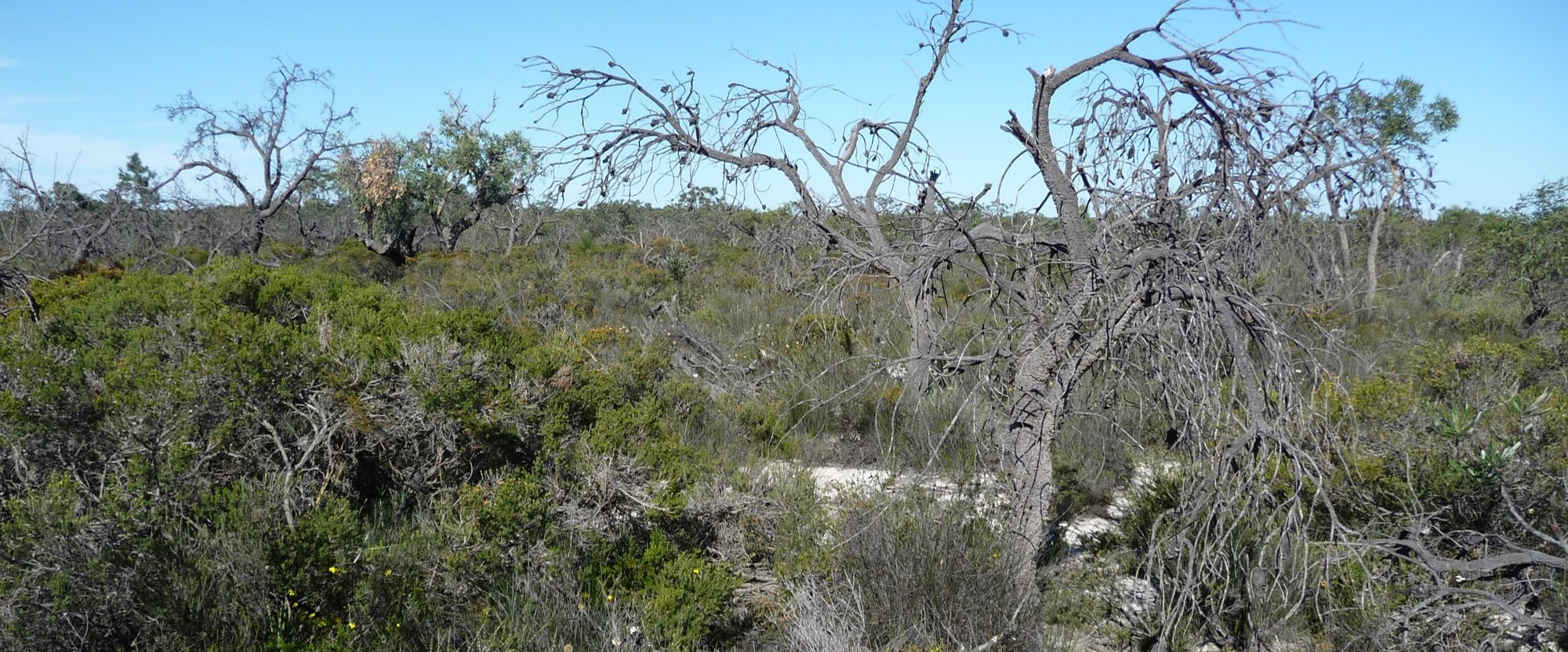
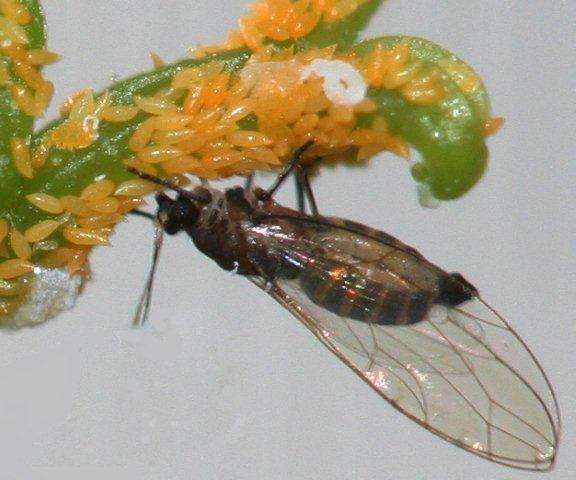
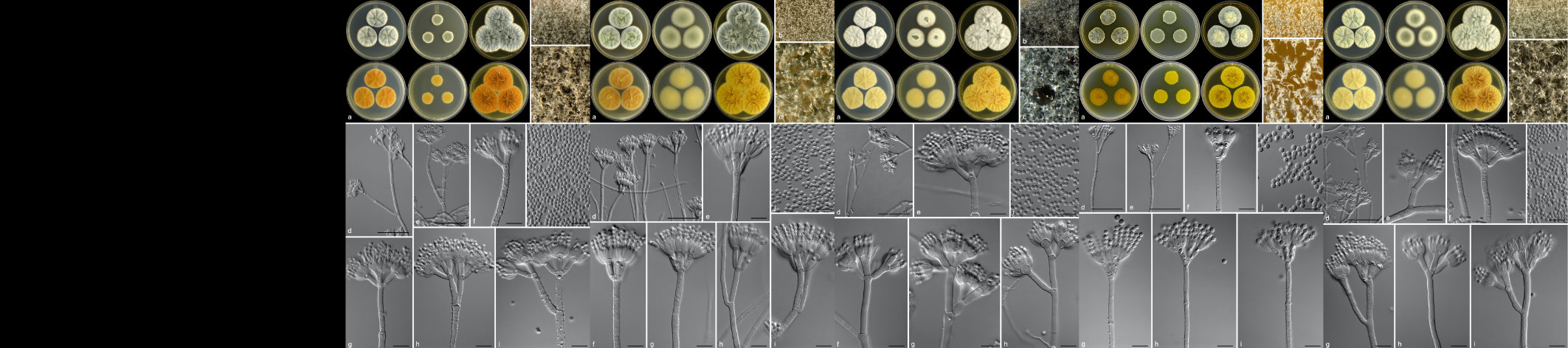
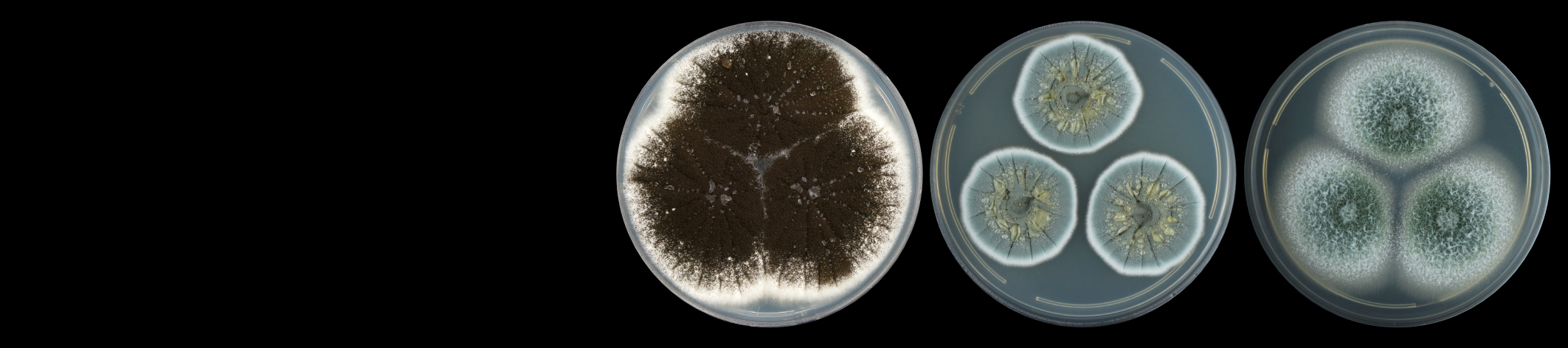
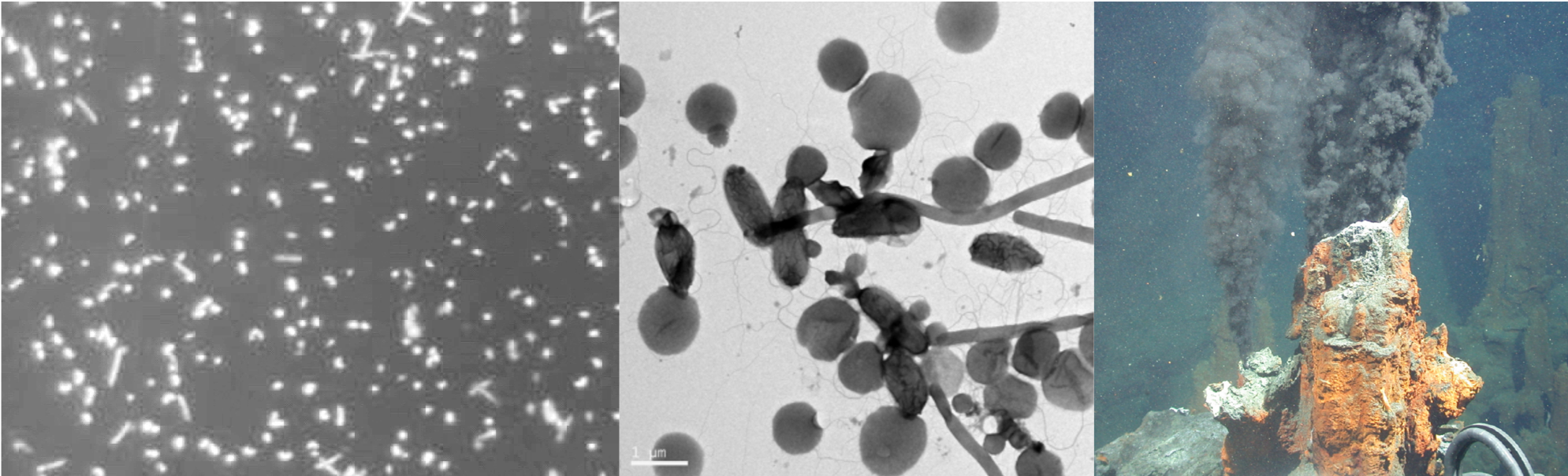
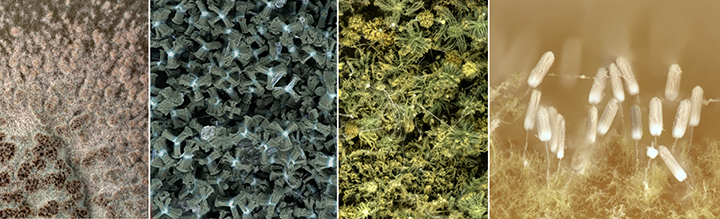
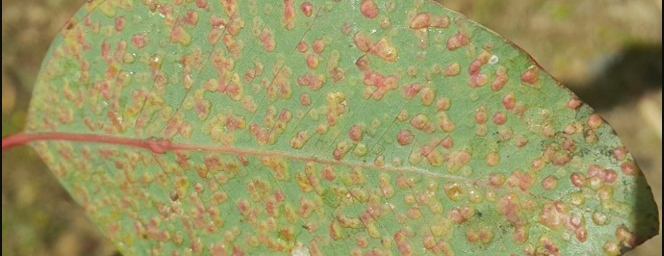
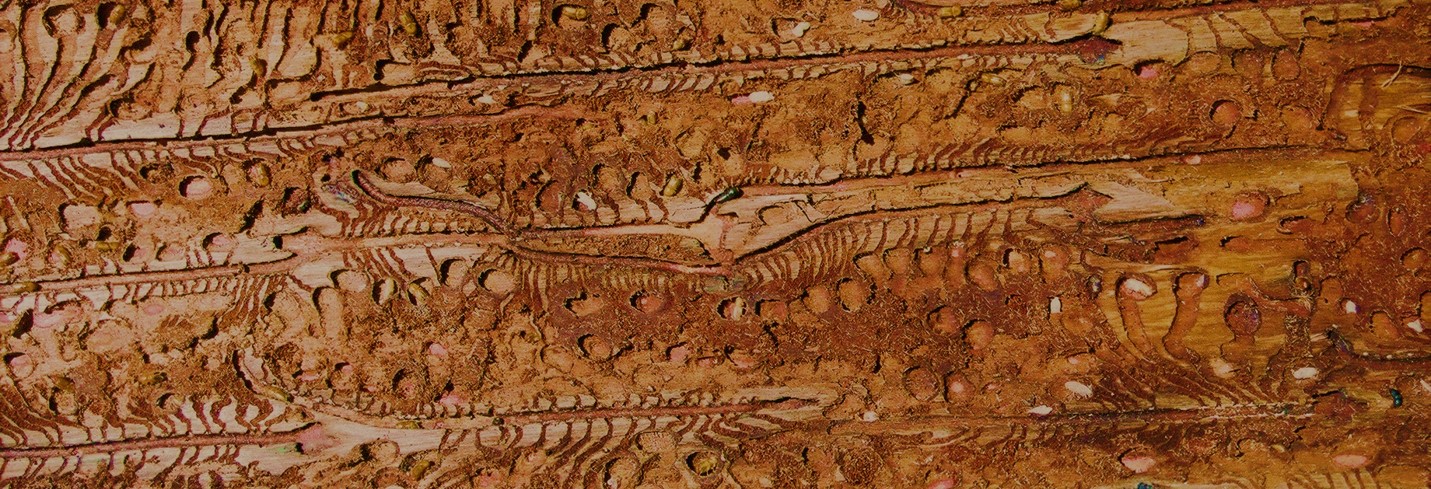
Viruses associations with plants often lead to growth and yield limiting disease symptoms, ultimately leading to economic losses and continue to pose a threat to food security, especially in the developing world. As there are no products which can be applied to plants in the field to control viral diseases in a manner equivalent to fungicides to control fungal diseases, control of viral diseases is generally achieved by the use of resistant plants or by controlling the spread of the virus between plants. In order to do this the epidemiology of the disease must be understood and control interventions applied at strategic points in the disease cycle. The Plant Virology Group focuses on determining the epidemiology and population dynamics of known viruses as well as the discovery of novel plant viruses and implementation of appropriate diagnostic assays for their detection. The plants under study are diverse and include species of agricultural importance and potential reservoir hosts, as well as native species. The majority of known plant viruses are associated with crops, however, even with important crop species, the associated viral diversity is likely to be grossly underestimated. While it is becoming apparent that not all plant virus infections result in severe, growth-limiting symptoms, especially on wild hosts, these viruses may pose a threat to agricultural crops through host jumps, leading to emerging viral diseases. Recent advances in DNA sequencing technologies have allowed for a paradigm shift for the discovery of novel plant virus diversity, as well as reshaping existing ideas of viral evolution and the interactions with their hosts.
Since the discovery of the first plant viruses, thousands of species have been characterised, a significant proportion of which have been characterised with the aid of metaviromics. In the last decade close to 500 new viruses have been recognised, with the genomic data of hundreds of “unclassified” viruses being deposited into public databases. However, the number of viruses that are officially recognised has been described as the tip of the iceberg and it is only recently that plant virologists are starting to appreciate the diversity of viruses as they are beginning to emerge at an alarming rate from wild hosts and their spread exacerbated by a surge in the global trade of plants.
In terms of public health, economics and virological research, SARS-CoV-2, which causes COVID-19, is arguably one of the most important viruses of the last century. The importance of the pandemic that has infected over 100 000 000 people cannot be understated. However, the fact that 822 000 000 people are currently facing food insecurity due to the effects of pests and diseases, 40% of which are viruses should not be dismissed. Therefore, at a time when food security on the African continent is coming under increasing threat from pests and diseases, including disproportionate pressure from plant viruses when compared with the developed world, increased surveillance and diagnostic development for their detection is crucial. The Plant Health Centre, being developed as part of Innovation Africa @UP, has identified capacity building within this space as critically important. Members of the Plant Virology Group are committed building the research and services we offer government and industry partners as part of FABI and Innovation Africa @UP’s Plant Health Centre.