Vegetable Crop Biotechnology Platform
Bacterial Genomics and Plant Pathogen Interactions
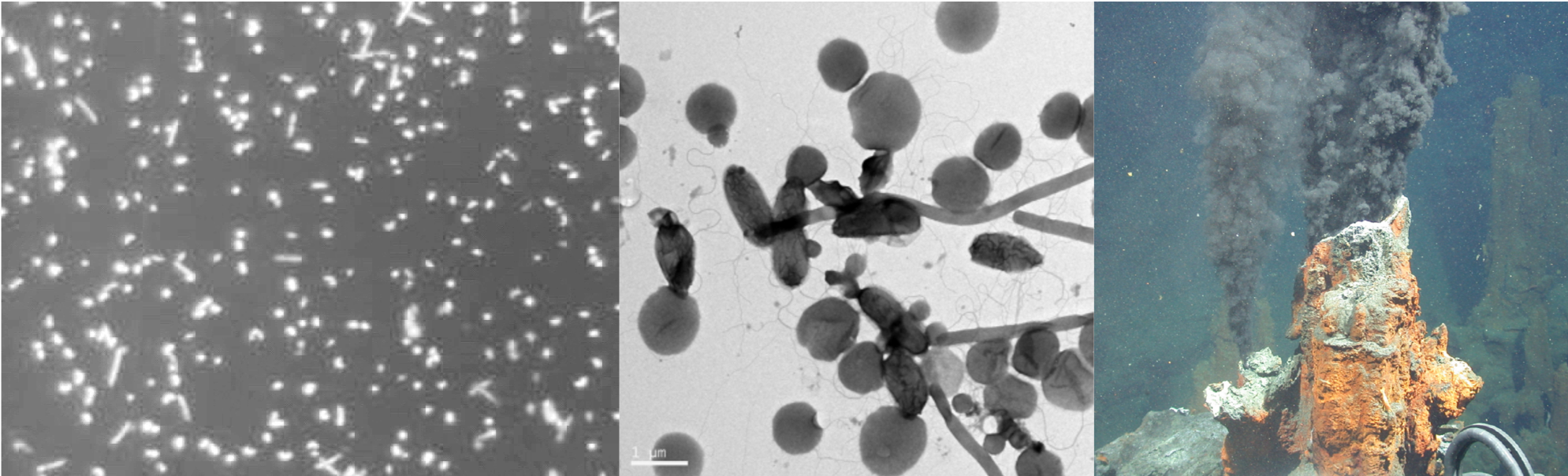
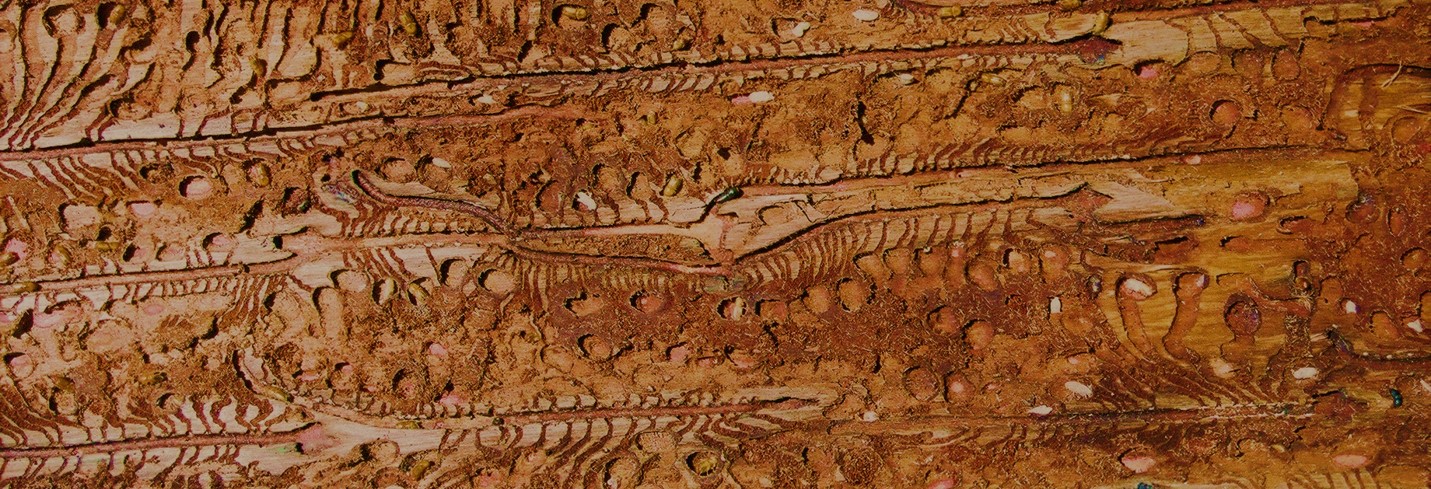
The bacterial genomics and host pathogen interactions research group is interested in understanding molecular pathogen-host interactions between potato plants and their various pathogens. The objectives of the research include molecular identification of potato pathogens and pests, functional characterisation of bacterial virulence factors and elucidation of potato plant responses elicited by potato pathogens. We ultimately endevour to contribute knowledge toward the control of pathogens and pests under study.
Potato Pathology Programme
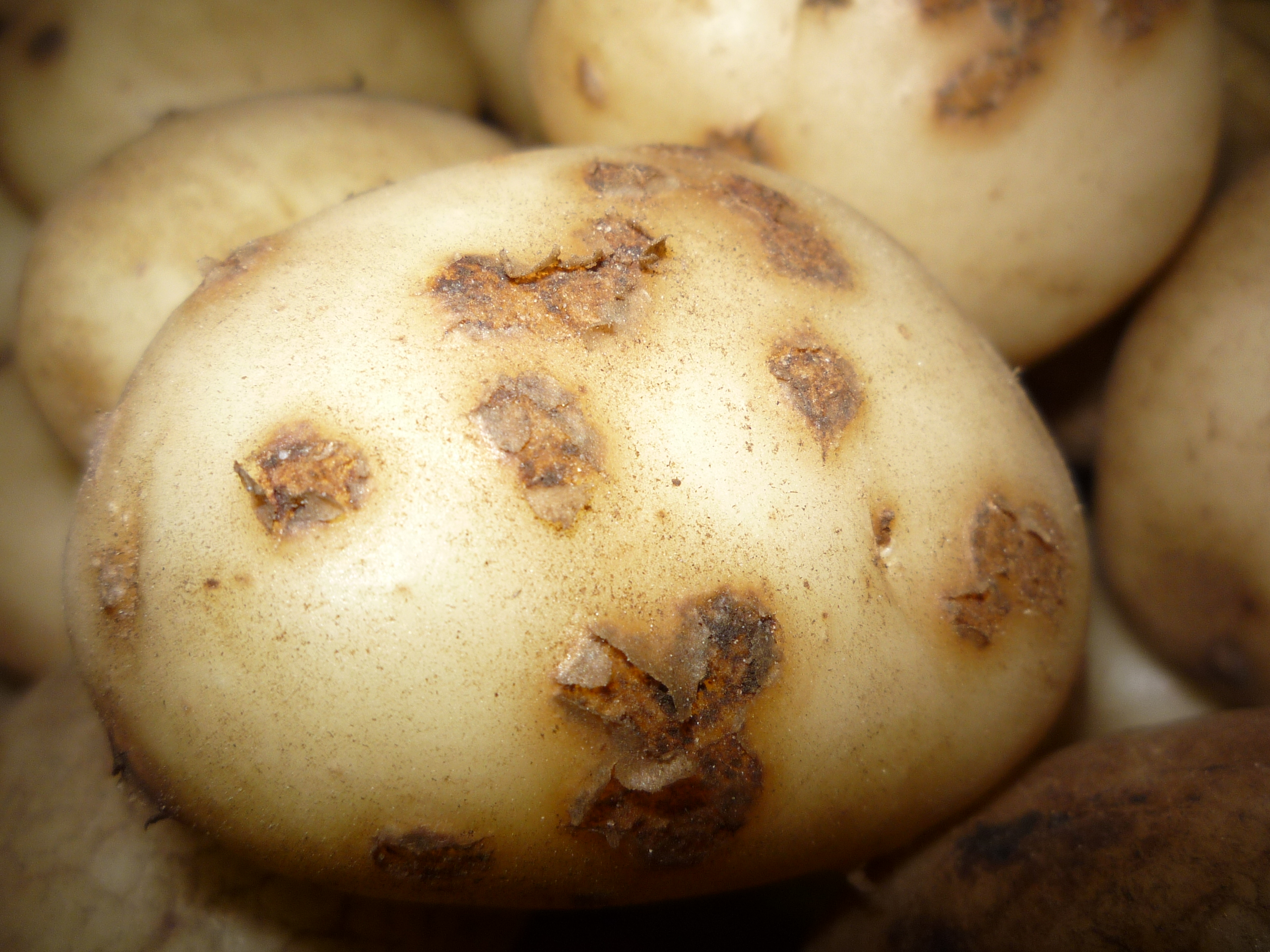
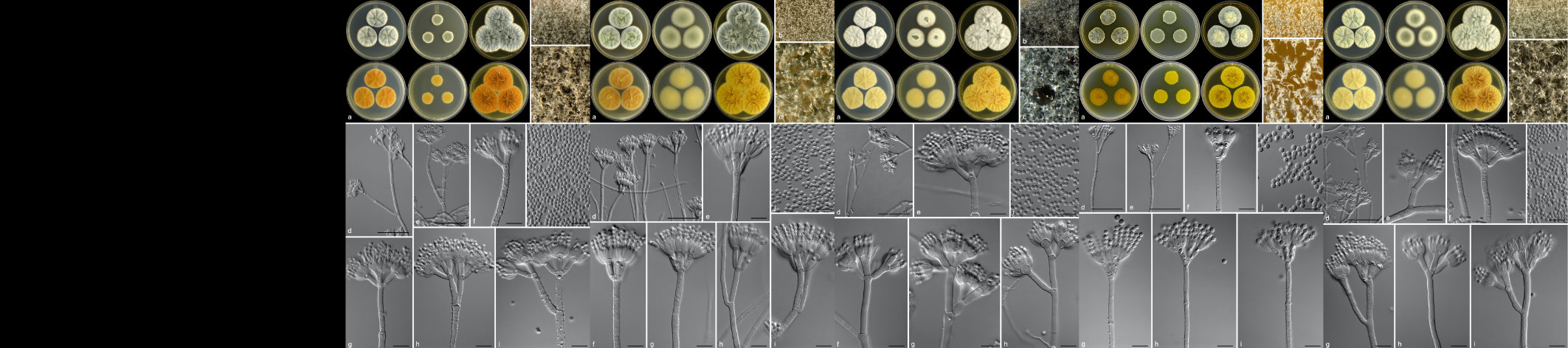
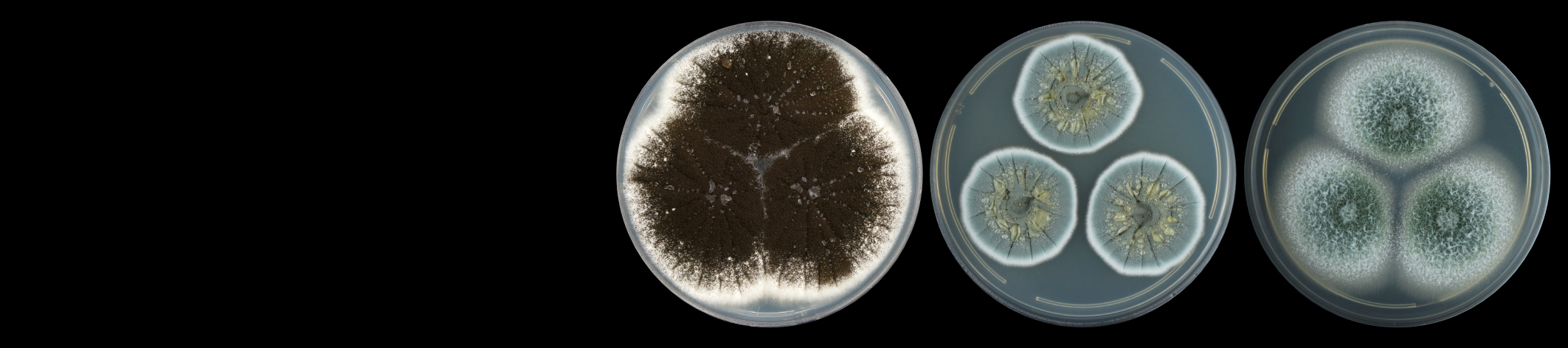
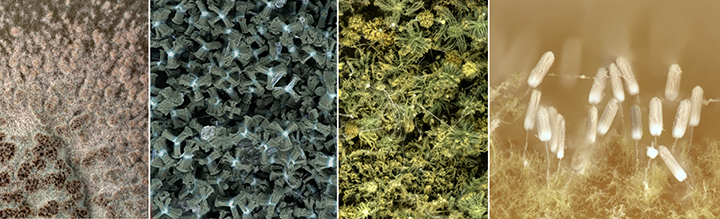
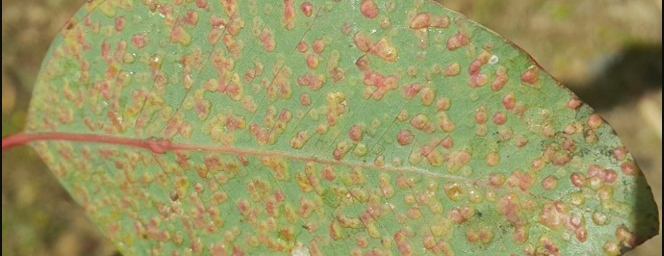
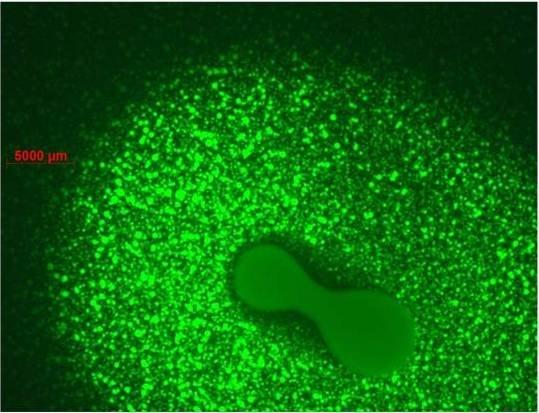
The primary research focus of the Potato Pathology Programme is the epidemiology, diagnosis and control of soil- and seed-borne diseases of potatoes. Diseases currently being investigated include powdery scab, black scurf, stem canker, blackleg and soft rot. Various approaches are used to better understand disease spread and development, host-pathogen interactions and control, to provide growers with risk assessment and disease management strategies.