Damage
Tree disease and death can arise from a multitude of factors, including living organisms (biotic) such as insects and fungi, or abiotic agents such as frost, drought and chemical damage. In order to adjust management practices appropriately, it is crucial to correctly identify the cause of damage to trees. The following section summarizes some of the most common causes of tree damage or disease and provides guidelines for distinguishing between the different categories of damage, disease and decline.
Distinguishing between causes of tree health problems
| Abiotic | Biotic | |
| Non-living (eg. chemicals, frost, drought) | Living (Fungi, bacteria, insects) | |
| Absence of host specificity | Often host specific | |
| Non-infectious | Infectious (can spread from one tree to another) | |
| Usually a gradient visible (worst near source of origin, with impact gradually becoming less as distance from source increases) Damage usually of same age/phase of expression |
Often random in the plantation Damage often at different stages of development as pathogen/pest spread from one tree to another |
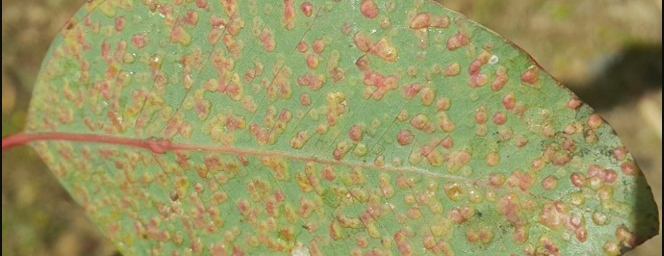
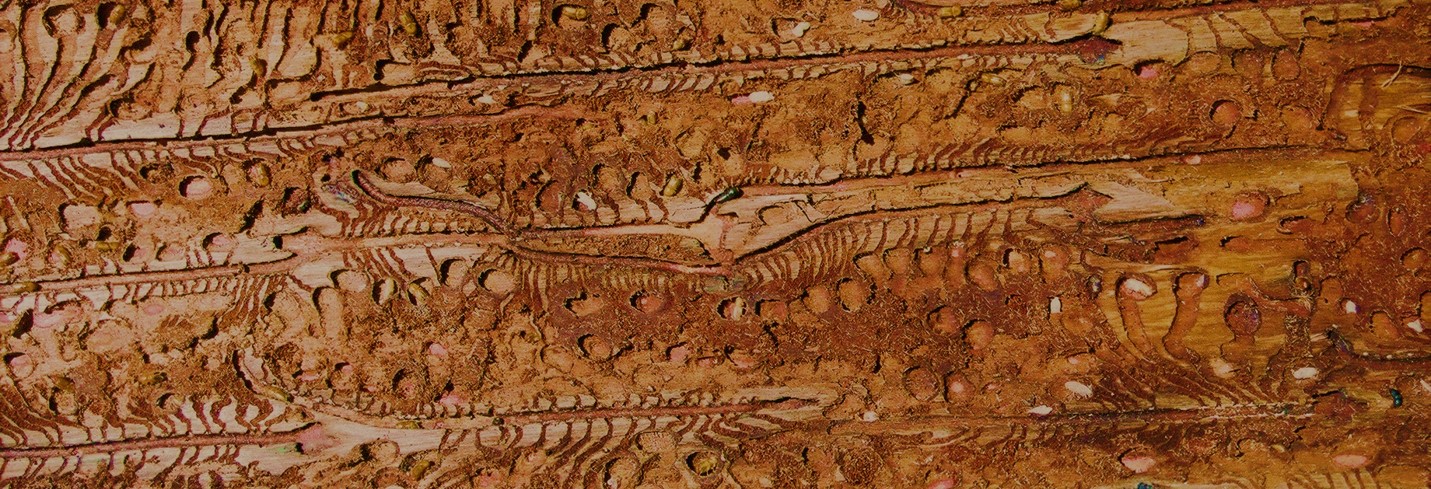
Signs and Symptoms
Disease and pest problems may be identified by observing certain signs and symptoms of infection / infestation. Signs include the presence of fungal fruiting bodies, or egg capsules of insects, while symptoms include leaf spots, defoliation, cracking of stems, wood stain etc. Characterizing the type of damage and the visible signs is useful in making accurate diagnoses.